Digital Forensics: Artifact Profile – WhatsApp Messenger

APPLICATION NAME: WhatsApp Messenger
CATEGORY: Chat
RELATED ARTIFACTS: WhatsApp Contacts, WhatsApp Messages
OPERATING SYSTEMS: iOS, Android
SOURCE LOCATION:
iOS – /root/var/mobile/Applications/net.whatsapp.WhatsApp/Documents/ChatStorage.sqlite
Android – /data/data/com.whatsapp/databases/msgstore.db
Android – /data/data/com.whatsapp/databases/wa.db
Android –/sdcard/WhatsApp/Databases/msgstore.db.crypt*
Importance to Investigators
Android
For Android devices, there are two SQLite databases of value for examiners recovering WhatsApp artifacts: msgstore.db and wa.db. The msgstore.db contains details on any chat conversations between a user and their contacts, whereas the wa.db stores information on all the WhatsApp user’s contacts.
The msgstore.db is a relatively simple SQLite database with two tables: chat_list and messages. The messages table contains a listing of all the messages that a user sends or receives from his/her contacts. Unlike Kik or BBM, where a user is required to have a unique username or PIN, WhatsApp uses the user’s phone number as a unique identifier for both the user and their contacts. This table includes the following and more:
- the contact’s phone number,
- message contents,
- message status,
- timestamps, and
- any details around attachments included in the message.
Attachments being sent through WhatsApp have their own table entry and the message contents will contain a null entry with a thumbnail and link to the photo/image being shared. This attachment is stored directly in the msgstore.db file. Additionally, the table may contain latitude and longitude coordinates for messages being sent, allowing the examiner to map out the geolocation details of a user.
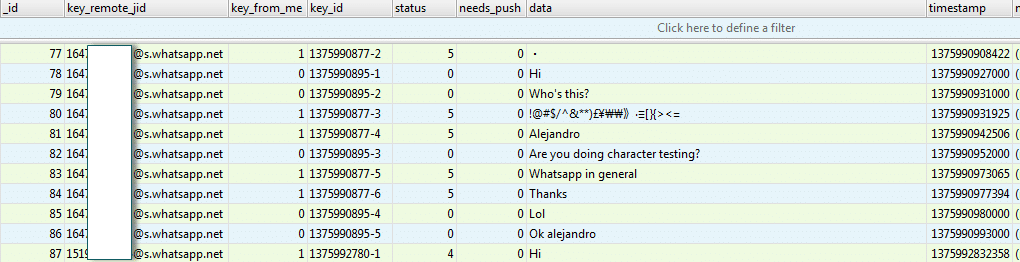
Screenshot of the WhatsApp chat_list table in msgstore.db.
The chat_list table contains a listing of all the phone numbers that a user communicated with. However, this is not a complete listing of the user’s contacts. For that we must look at the wa.db.
The wa.db contains a complete listing of a WhatsApp user’s contacts including phone number, display name, timestamp, and any other information given upon registering with WhatsApp.
In order to gain access to the msgstore.db and wa.db, an examiner must root or gain physical access to the Android device. Otherwise, WhatsApp also stores a copy of the msgstore.db on the SD card, which is used for backups and can be found at the following location:
/sdcard/WhatsApp/Databases/msgstore.db.crypt*
One caveat with this file is that it is encrypted and must be decrypted prior to analysis. WhatsApp uses several different types of encryption on this database depending on the version of WhatsApp being used. Examiners may come across different extensions that represent the encryption being used. Crypt, crypt5, crypt7, and crypt8 have all been identified as belonging to WhatsApp encrypted databases. These encrypted databases can be decrypted as long as the examiner is able to get the key, which is typically stored on the data partition in the WhatsApp folder.
Recovering WhatsApp contacts, messages, and attachments on Android is relatively straightforward once you have access to the appropriate databases. The process is similar in iOS with some minor differences.
iOS
Unlike Android, which uses multiple SQLite databases, iOS stores all relevant WhatsApp data in one database called ChatStorage.sqlite. You can find this database in the following location:
net.whatsapp.WhatsApp/Documents/ChatStorage.sqlite
The ZWAMESSAGE and ZWAMEDIAITEM tables are excellent locations for collecting items of evidentiary value including messages, sender, recipient, timestamps, geolocation data, and the path/location of any media being shared between two contacts. Many of the same artifacts mentioned for Android are found in these locations; however the table names and structure may be different.
In addition to the ChatStorage.sqlite database, there is also a Contacts.sqlite database in the same location. While there are some extra details about a user’s WhatsApp contacts, this database does not include the JID for each contact that uniquely identifies the user to the WhatsApp servers.
WhatsApp Recovery with Magnet Forensics
Magnet Forensics tools support the recovery of messages, contacts, and attachments from WhatsApp conversations on both Android and iOS. They will parse and carve the artifacts mentioned above and organize them for the examiner in a format that is easy to read and analyze. Below is a sample output from an Android WhatsApp message:
- Sender and receiver details
- The message contents
- Message status
- All available timestamps
- Geolocation data (if available)
- Thumbnail/attachment image and details
Magnet Forensics will recover and analyze both the unencrypted databases from a rooted or file system image or the tools can also decrypt the encrypted version found on the SD card for Android devices. They will automatically decrypt WhatsApp databases using crypt, crypt5, crypt7, and crypt8 as long as it is given access to where the key is stored.